Introduction
Ribosomes are small, non-membrane-bound organelles found in all living cells. They are the sites of protein synthesis, making them essential for cell growth, repair, and metabolism.
Discovery
Ribosomes were discovered by George Emil Palade and are also known as Palade particles.
Structure of Ribosomes
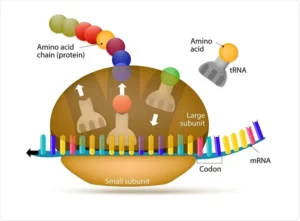
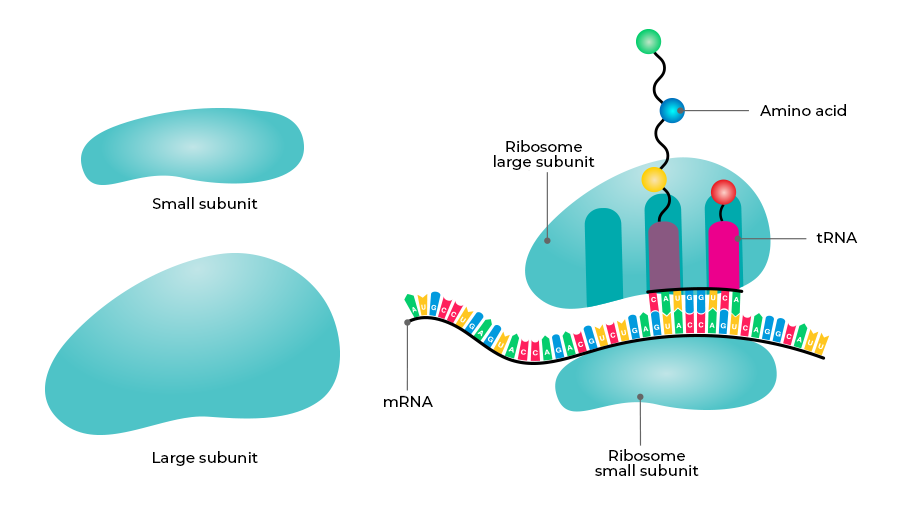


• Ribosomes are composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins • They have two subunits – large and small • Not surrounded by a membrane • Found either free in cytoplasm or attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum
Types of Ribosomes
1. 70S Ribosomes
• Found in prokaryotes • Also present in mitochondria and chloroplasts of eukaryotes • Made of 50S (large) + 30S (small) subunits
2. 80S Ribosomes
• Found in eukaryotic cytoplasm • Made of 60S (large) + 40S (small) subunits
Location of Ribosomes
• Free ribosomes – synthesize proteins used inside the cell • Bound ribosomes – synthesize proteins for secretion or membranes
Functions of Ribosomes
Protein synthesis
Help in enzyme formation
Essential for growth and repair
Support metabolic activities
Ribosomes vs Lysosomes (Quick Comparison)
• Ribosomes: Protein synthesis • Lysosomes: Digestion and waste removal
Diagram (To be added)
Labeled diagram of ribosome structure
Key Points for Exams
• Ribosomes are non-membranous • Present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells • Called protein factories of the cell • rRNA plays a catalytic role
5 MCQs
1. Ribosomes are the site of: A) Respiration
B) Protein synthesis
C) Digestion
D) Transport
Answer: B
2. Ribosomes are composed of: A) DNA & proteins
B) rRNA & proteins
C) Lipids & proteins
D) Enzymes only
Answer: B
3. 80S ribosomes are found in: A) Prokaryotes
B) Mitochondria
C) Eukaryotic cytoplasm
D) Chloroplast
Answer: C
4. Who discovered ribosomes? A) Robert Hooke
B) Watson
C) Palade
D) Golgi
Answer: C
5. Ribosomes attached to RER synthesize: A) Cytoplasmic proteins
B) Secretory proteins
C) Lipids
D) ATP
Answer: B
