Tag: A level biology

General Q&A part-6
State two features of the gas exchange surface in humans? The gas exchange surface in humans primarily refers to the respiratory system, where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. Two essential features of the gas exchange surface in humans are: Large Surface Area: The gas exchange surface in humans, which includes the…

DNA Replication
DNA replication is a fundamental process in biology that ensures the faithful duplication of genetic information. It involves multiple steps and a variety of enzymes and proteins working together to ensure accuracy. Here’s a more in-depth breakdown of the process: Initiation: DNA replication begins at specific sites on the DNA molecule known as origins of…

Reproduction in Organisms
Reproduction is a fundamental biological process that ensures the continuation of life on Earth. It is a fascinating and diverse field of study, as organisms have evolved a wide range of strategies to reproduce and pass on their genetic material to the next generation. In this educational blog, we will explore the various mechanisms of…

Q&A on Kingdom Monera
Q: What is Kingdom Monera? A: Kingdom Monera is one of the five biological kingdoms, encompassing prokaryotic microorganisms, which include bacteria and archaea. Q: What defines prokaryotic microorganisms in Kingdom Monera? A: Prokaryotic cells in Kingdom Monera lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, and they typically possess a singular circular chromosome. Q: How do…

Kingdom Monera
In the vast tapestry of life on Earth, Kingdom Monera stands as a remarkable and often underestimated realm. Comprising some of the tiniest yet most impactful organisms on the planet, this kingdom is teeming with diversity and significance. In this blog, we will explore the captivating world of Kingdom Monera, its defining characteristics, diversity, and…

Q&A on plant kingdom
The world of plants is a rich and diverse one, with countless species that span the globe, from the tallest trees to the tiniest mosses. Understanding the plant kingdom is not only fascinating but also essential to our understanding of the natural world. In this Q&A on the plant kingdom, we will delve into the…

General Q&A part-5
What are the stages involved in PCR, and on what does PCR depend? Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a widely used molecular biology technique for amplifying specific DNA sequences. PCR involves several stages, and it depends on various components and conditions for successful amplification. Here are the main stages of PCR and what PCR depends…

The Living World and Taxonomy
Biodiversity The variety of life forms present on Earth, including the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms, their genetic variation, and the ecosystems they form. Species A group of individuals that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring in nature; the basic unit of biological classification. Taxonomy The science of naming, defining, and classifying organisms…

Q&A on Glycolysis
1. What is glycolysis, and why is it important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose into energy-rich molecules. It’s crucial for energy production in cells. 2. Where does glycolysis occur in cells? Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of cells. 3. How many ATP molecules are initially invested in glycolysis? Two ATP…

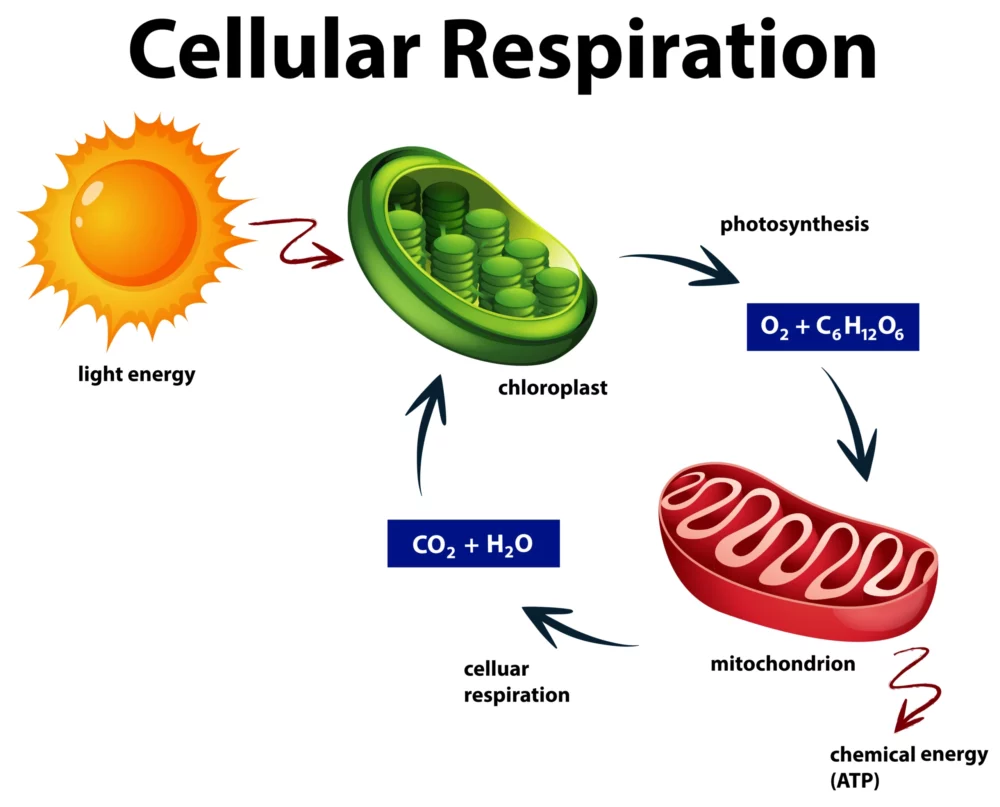
Cellular Respiration: A Simplified Guide
Cellular respiration, found in all living organisms, is a fascinating but intricate biological process. At its core, it’s how cells generate the energy needed to power various life functions. In this simplified guide, we’ll unravel the mysteries of cellular respiration, making it accessible to everyone, regardless of your scientific background. The Basics: What Is Cellular…

Q&A on Cell organelles
Q: What are cell organelles? A: Cell organelles are specialized structures within a cell that perform specific functions. They are often referred to as the “organs” of a cell because they carry out various tasks necessary for the cell’s survival and function. Q: What is the function of the cell membrane? A: The cell membrane,…

General Biology MCQs
Here are some biology MCQs. 1. Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells? a) Mitochondria b) Nucleus c) Chloroplasts d) Endoplasmic reticulum Answer: c) Chloroplasts Explanation: Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis, where plants convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose. 2. Which of the following is NOT a…