Category: Biochemistry

General Q&A part-6
State two features of the gas exchange surface in humans? The gas exchange surface in humans primarily refers to the respiratory system, where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. Two essential features of the gas exchange surface in humans are: Large Surface Area: The gas exchange surface in humans, which includes the…

DNA Replication
DNA replication is a fundamental process in biology that ensures the faithful duplication of genetic information. It involves multiple steps and a variety of enzymes and proteins working together to ensure accuracy. Here’s a more in-depth breakdown of the process: Initiation: DNA replication begins at specific sites on the DNA molecule known as origins of…

General Q&A part-5
What are the stages involved in PCR, and on what does PCR depend? Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a widely used molecular biology technique for amplifying specific DNA sequences. PCR involves several stages, and it depends on various components and conditions for successful amplification. Here are the main stages of PCR and what PCR depends…

Q&A on Glycolysis
1. What is glycolysis, and why is it important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose into energy-rich molecules. It’s crucial for energy production in cells. 2. Where does glycolysis occur in cells? Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of cells. 3. How many ATP molecules are initially invested in glycolysis? Two ATP…

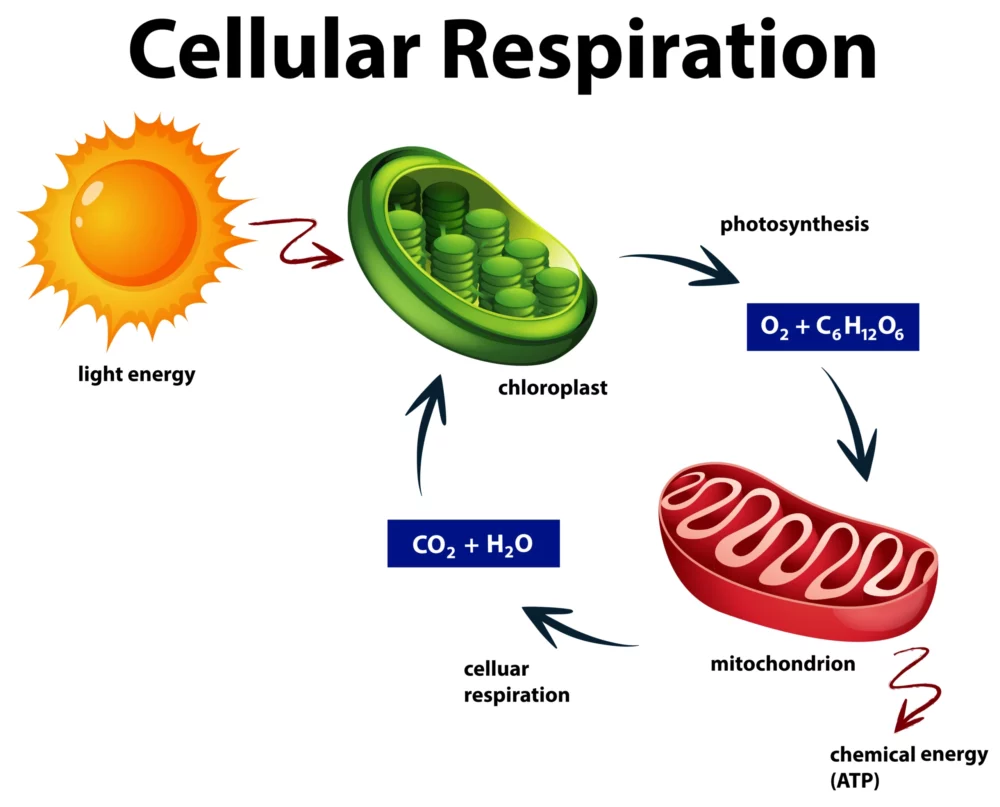
Cellular Respiration: A Simplified Guide
Cellular respiration, found in all living organisms, is a fascinating but intricate biological process. At its core, it’s how cells generate the energy needed to power various life functions. In this simplified guide, we’ll unravel the mysteries of cellular respiration, making it accessible to everyone, regardless of your scientific background. The Basics: What Is Cellular…

General Biology MCQs
Here are some biology MCQs. 1. Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells? a) Mitochondria b) Nucleus c) Chloroplasts d) Endoplasmic reticulum Answer: c) Chloroplasts Explanation: Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis, where plants convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose. 2. Which of the following is NOT a…

General Q&A part-4
What is oncology? Oncology is the branch of medicine that specializes in the study, diagnosis, treatment, and research of cancer. Cancer is a complex group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. Oncologists are medical professionals who are trained to diagnose and treat various types of cancer,…

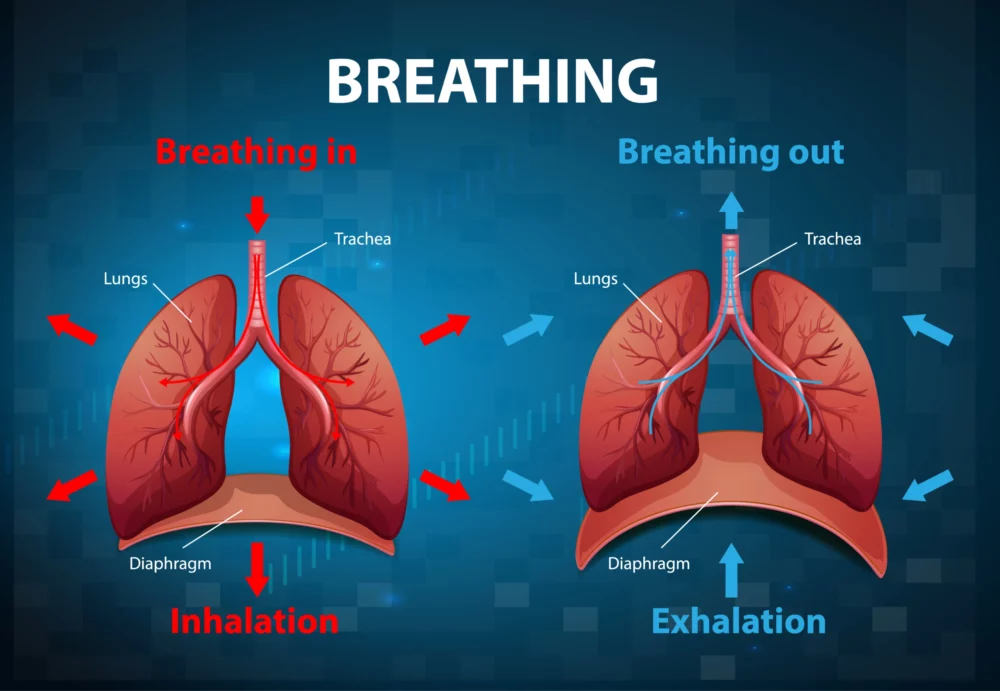
The Respiratory Puzzle: Gaseous Exchange vs. Breathing
Respiration is a fundamental process for all living organisms, ensuring the supply of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide, critical for sustaining life. While “breathing” is a term we commonly associate with the respiratory process, it is essential to recognize that respiration is a multifaceted concept, involving both mechanical actions and intricate physiological processes.…

General Q&A part-2
This page contains general Q&A questions asked by curious people. What is biochemistry? Biochemistry is a branch of science that combines principles from both biology and chemistry to study the chemical processes and substances that occur within living organisms. It focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms that underlie various biological functions and processes, including metabolism,…

General Q&A part-1
This page contains general Q&A questions asked by curious people. How many types of Air pollution? Air pollution can be categorized into several types based on the sources of pollutants, the nature of the pollutants, and their effects on the environment and human health. The main types of air pollution include: Particulate Matter (PM): Particulate…

What is enzyme and characteristics?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions in living organisms. They are typically proteins, although some RNA molecules also have catalytic activity. Enzymes are essential for life because they speed up the reactions that are necessary for cells to function properly. Without enzymes, many biochemical reactions in the body would occur too slowly to…

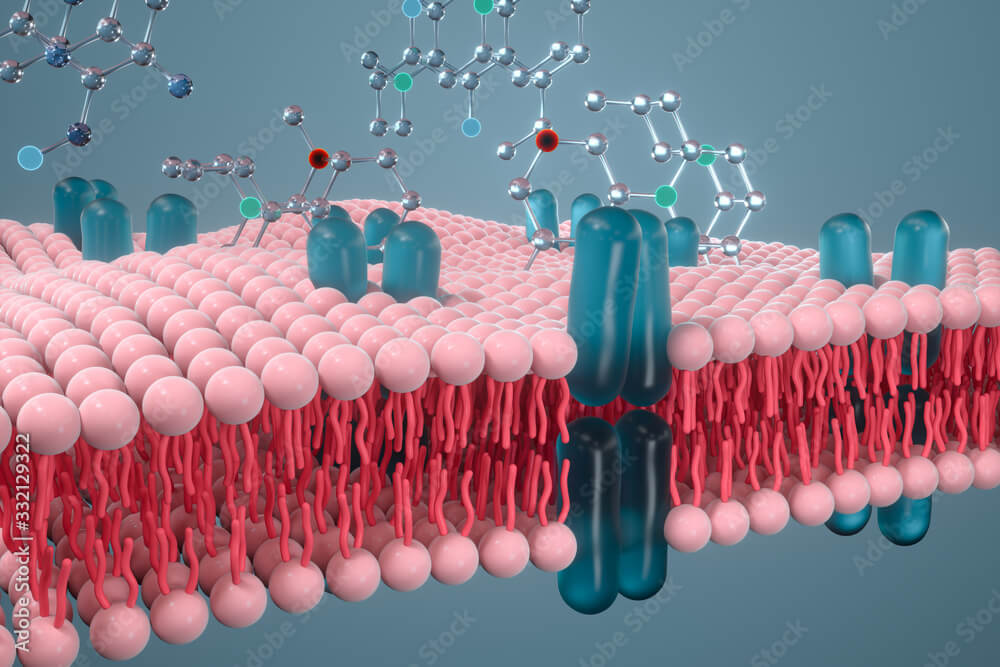
Plasma membrane
Delimiting membrane or boundary of all cells providing the characteristic shape to the cell. Structure ● Composed of approx. 7 nm thick phospholipid bilayer with hydrophilic heads facing outward from both sides into aqueous environment and hydrophobic tails facing inside the bilayer. ● A symmetrical the presence of proteins, floating in the bilayer imparts a…