Category: Biochemistry

Mutation
Mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of an organism’s genetic material. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule that carries the genetic instructions for the development and function of all living things. DNA is made up of four chemical bases, adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T), which are arranged in…

Chromosome
A chromosome is a structure found in cells that is made up of a long strand of DNA, which is the genetic material that contains the instructions for the development and function of all living organisms. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and play a crucial role in the cell cycle, replication,…

True Or False On Carbohydrates

MCQ on Respiration in plant
Q1: Which organelle in plant cells is primarily responsible for cellular respiration? (A) Chloroplast (B) Mitochondrion (C) Vacuole (D) Nucleus Answer: (B) Mitochondrion Explanation: Mitochondria are the main sites of cellular respiration in plant cells, where ATP is produced. Q2: During respiration, what is the primary substrate used by plants to generate energy? (A) Oxygen…

BLOOD CLOTTING (HAEMOSTASIS)
The clot or coagulam is a dark -reddish-brown ‘scum’ formed mainly by a network of threads in which dead or damaged blood elements are trapped. It is the property of plasma. Normal blood clotting time is 3−10 min. The clot inside the blood vessels is called a thrombus. A moving thrombus is called embolus. In…

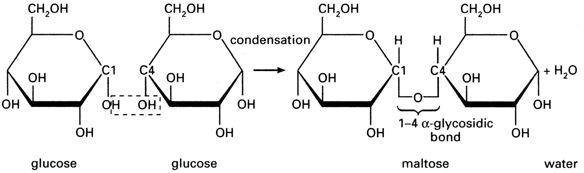
CARBOHYDRATES
Table of Contents Carbohydrates are classified into two types on the basis of molecular weight. Micromolecules – Monosaccharides and Oligosaccharides (Including Disaccharides) Macromolecules – Polysaccharides The micromolecules have the molecular weight of < 1000 Daltons whereas themacromolecules have > 1000 Daltons as molecular weight. Why do we need carbohydrates in our food? Carbohydrates provides about…
MCQs ON PLANT KINGDOM
1. Sexual reproduction involving the fusion of two cells in Chlamydomonas is (a) isogamy (b) homogamy (c) somatogamy (d) hologamy Answer and Explanation: 1. (d): Isogamy involves the fusion of gametes which are morphologically and physiologically similar. They are called isogametes. In Chlamydomonas, two vegetative cells may fuse to form a zygospore and the phenomenon is…

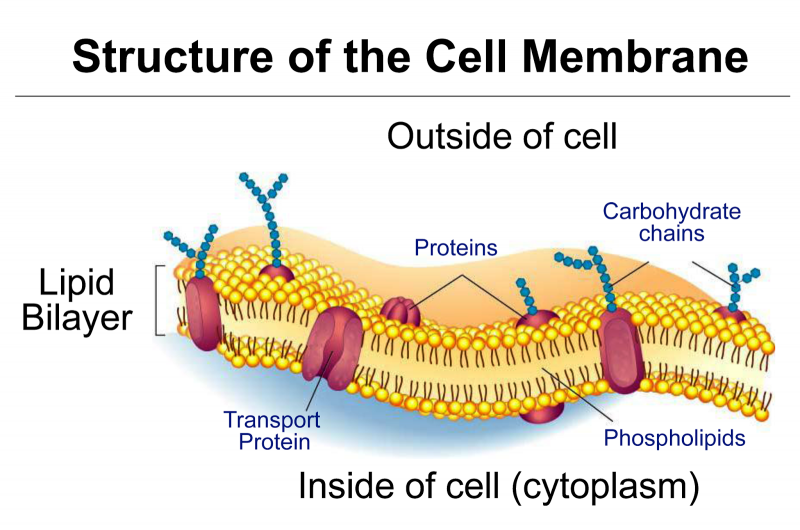
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is otherwise called a Plasma membrane. It may be defined as the thin, elastic, semipermeable living membrane that serves as a boundary for the Cytoplasm. The Cell membrane is made up of glycoproteins and phospholipids. The Functions of the Cell membrane are as follows: Cell membrane or Plasma membrane is a semipermeable membrane present…
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION, ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION It is the main source of energy of our cell. Takes place in Mitochondria. Movement of protons through inner mitochondrial membrane leads to ATP production DEFINITION Oxidative phosphorylation includes the coupling of the oxidation of NADH or FADH2 by the respiratory chain with the synthesis of ATP via gradient of protons across the inner mitochondrial…
Q & A ON WATER AND MINERAL SALT
Q1. What is the approximate percentage (in mass) of water in the human body? Is this percentage expected to be larger in the adult or in the old individual? Ans: Approximately 65% of the human individual mass is water. The brain, for example, has around 90% of water in mass, the muscles, 85%, and the…

VARIETY OF LIFE
Q1) Any attribute or descriptive phrase, referring to form, structure or behaviour of a specific organism for a particular purpose is: A) Expression B) Specificity C) Character D) Nature E) None of the above Q2) Which one of the following is an example of “Expression of character”? A) Petal length B) Stem thickness C) Corolla…

ENZYMES
Q1) Enzyme is a Greek word which means: A) in virus B) in bacteria C) in fungi D) in yeast E) in humans Q2) Who discovered that certain molecules of ribonucleic acid also function as enzymes? A) Friedrich Wilhem Kuhne only B) Friedrich and Thomas Cech C) Thomas Cech only D) Sidney Altman & Thomas…