Chapter: Cell – The Unit of Life
Unit: Cell Biology
Exam Focus: NEET (High-Yield Comparison Topic)
Introduction
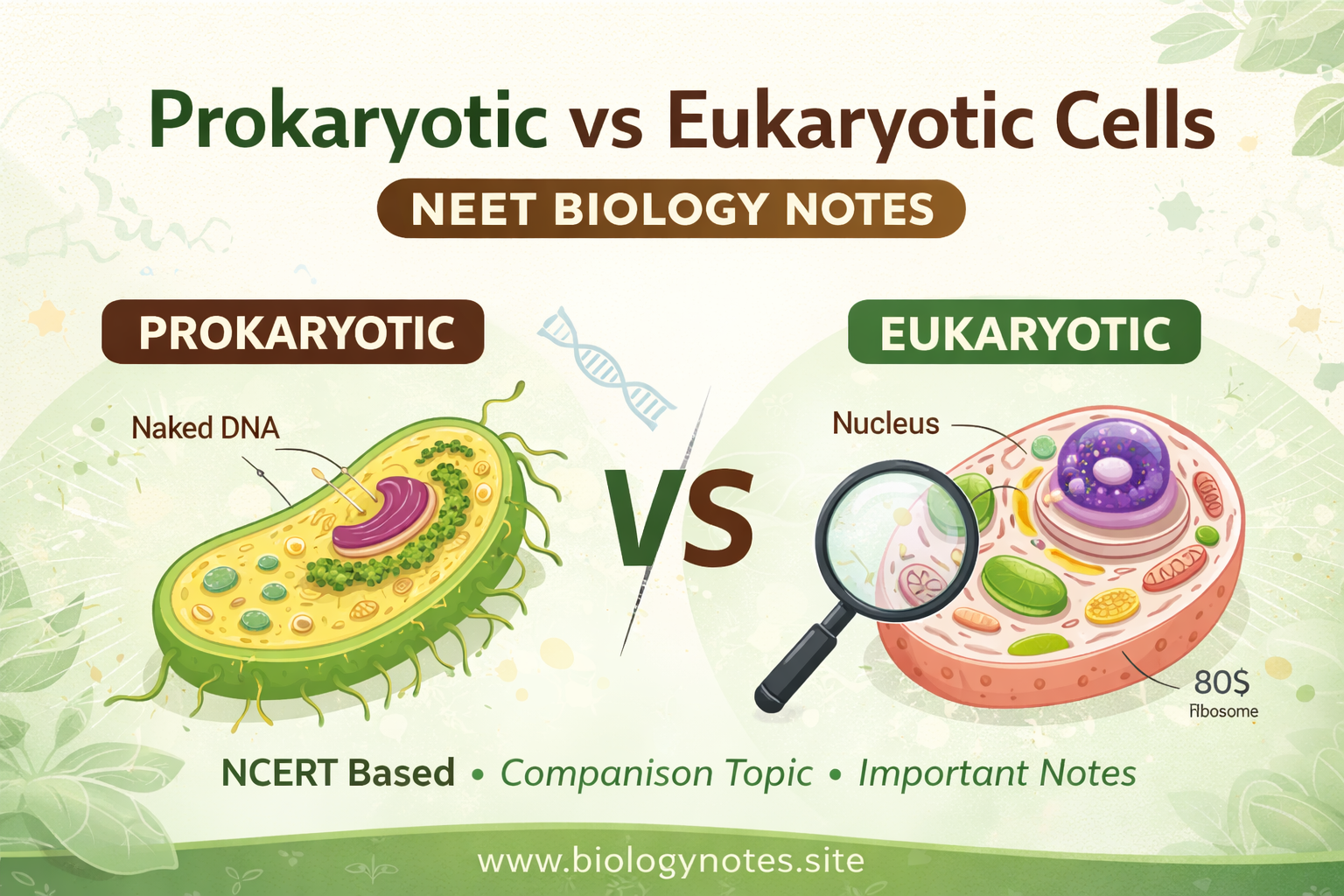
Living organisms are made up of cells that are broadly classified into prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
The main difference between them lies in the presence or absence of a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Understanding this comparison is extremely important for NEET, as it is frequently tested through MCQs and match-the-following questions.
What are Prokaryotic Cells?
Prokaryotic cells are simple and primitive cells that lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Key Features
No nuclear membrane
Genetic material is naked DNA
Organelles like mitochondria, ER, Golgi are absent
Ribosomes are 70S
Cell wall usually made of peptidoglycan
Examples
Bacteria
Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae)
Mycoplasma
What are Eukaryotic Cells?
Eukaryotic cells are complex cells that have a well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Key Features
True nucleus with nuclear membrane
DNA is associated with histone proteins
Membrane-bound organelles present
Ribosomes are 80S
Larger in size compared to prokaryotes
Examples
Plant cells
Animal cells
Fungi
Protists
Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (NEET Table)
| Feature | Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Nuclear membrane | Absent | Present |
| DNA | Circular, naked | Linear, with histones |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Absent | Present |
| Ribosomes | 70S | 80S |
| Cell size | Small (1–10 µm) | Large (10–100 µm) |
| Cell division | Binary fission | Mitosis / Meiosis |
NEET Important Points ⭐
Mesosomes are infoldings of plasma membrane in prokaryotes
Plasmids are extra-chromosomal DNA in bacteria
Mycoplasma is the smallest living cell
Prokaryotic cells do not show mitosis
Common NEET Traps ⚠️
❌ Ribosomes in mitochondria and chloroplasts are 70S, not 80S
❌ Prokaryotes do not have membrane-bound organelles
✔ Plant cells are eukaryotic despite having a cell wall
✔ Bacterial DNA is not enclosed by a nuclear membrane
Quick Revision Box ⏱️
Prokaryotes → No nucleus, no organelles
Eukaryotes → True nucleus present
70S ribosomes → Prokaryotes
80S ribosomes → Eukaryotes
Binary fission → Prokaryotes
NEET Practice MCQs
Q1. Ribosomes present in prokaryotic cells are:
A) 80S
B) 60S
C) 70S
D) 90S
Answer: C
Q2. Which of the following is a prokaryote?
A) Amoeba
B) Paramecium
C) Bacteria
D) Yeast
Answer: C
Q3. Mesosomes are associated with:
A) Nucleus
B) Mitochondria
C) Plasma membrane
D) Ribosomes
Answer: C
One-Line NEET Takeaway ⭐
The presence of a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles distinguishes eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.