Tag: Oxydative phosphorylation

OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION, ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
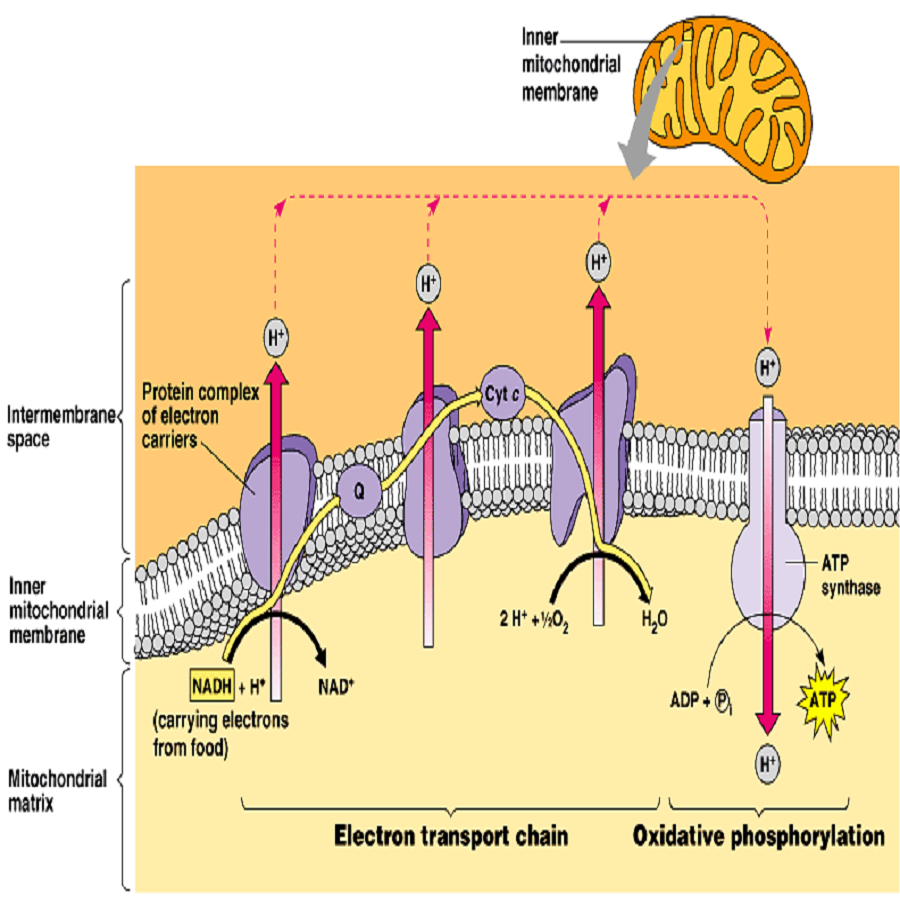
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION It is the main source of energy of our cell. Takes place in Mitochondria. Movement of protons through inner mitochondrial membrane leads to ATP production DEFINITION Oxidative phosphorylation includes the coupling of the oxidation of NADH or FADH2 by the respiratory chain with the synthesis of ATP via gradient of protons across the inner mitochondrial…

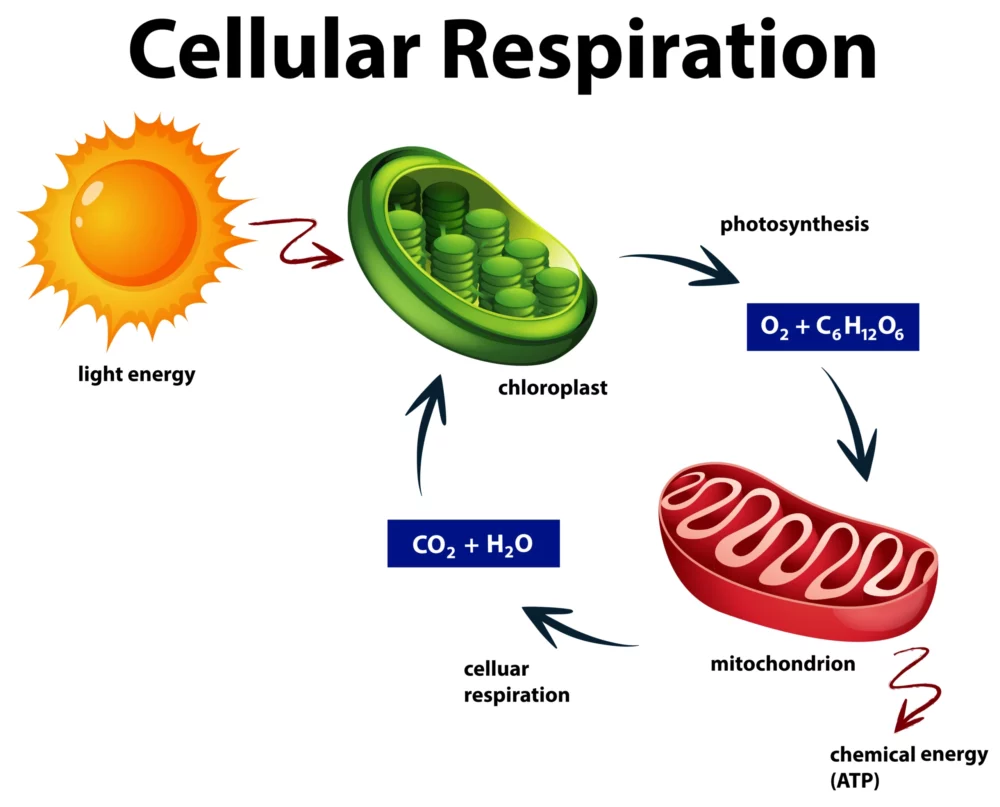
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Cellular respiration is a fundamental biochemical process that occurs in all living cells, from the tiniest bacteria to the most complex multicellular organisms. It is the means by which cells convert organic molecules, primarily glucose, into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – the universal currency of cellular energy. This intricate and highly regulated metabolic pathway is essential…