Category: A level biology

Defences Against Diseases
The body has three main lines of defence against disease. These involve mechanical barriers, chemical barriers and cells. Mechanical barriers Although many bacteria live on the surface of the skin, the outer layer of the epidermis seems to act as a barrier that stops them getting into the body. But if the skin is cut…

Sir Alexander Fleming
(August 6 , 1881 – March 11, 1955) Early life and Education Sir Alexander Fleming was a Scottish physician, microbiologist, and pharmacologist, who was born on August 6, 1881 at Lochfield farm near Darvel, in Ayrshire, Scotland. Alexander was the third of four children of farmer Hugh Fleming (1816–1888) from his second marriage to Grace…

True Or False On Carbohydrates

Types of Classification System
Biological classification is the scientific procedure of arranging organisms into groups on the basis of their similarities and dissimilarities and placing the groups in a hierarchy of categories like species, genus, family, etc

MCQ on Respiration in plant
Q1: Which organelle in plant cells is primarily responsible for cellular respiration? (A) Chloroplast (B) Mitochondrion (C) Vacuole (D) Nucleus Answer: (B) Mitochondrion Explanation: Mitochondria are the main sites of cellular respiration in plant cells, where ATP is produced. Q2: During respiration, what is the primary substrate used by plants to generate energy? (A) Oxygen…
Osmosis
If a dilute solution is separated from a concentrated solution by a partially permeable membrane, water diffuses across the membrane from the dilute to the concentrated solution. This is known as osmosis. A partially permeable membrane is porous but allows water to pass through more rapidly than dissolved substances. Since a dilute solution contains, in…

Q & A ON REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
Q1. What is life span? Ans: Life span is the period from birth to natural death of an organism. Q2. Define clone. Ans: The individuals that are morphologically and genetically similar to the parent are called clone. Q3. Mention the different means/ methods of asexual reproduction with example. Ans: Cell division – Protista, Monera Binary…

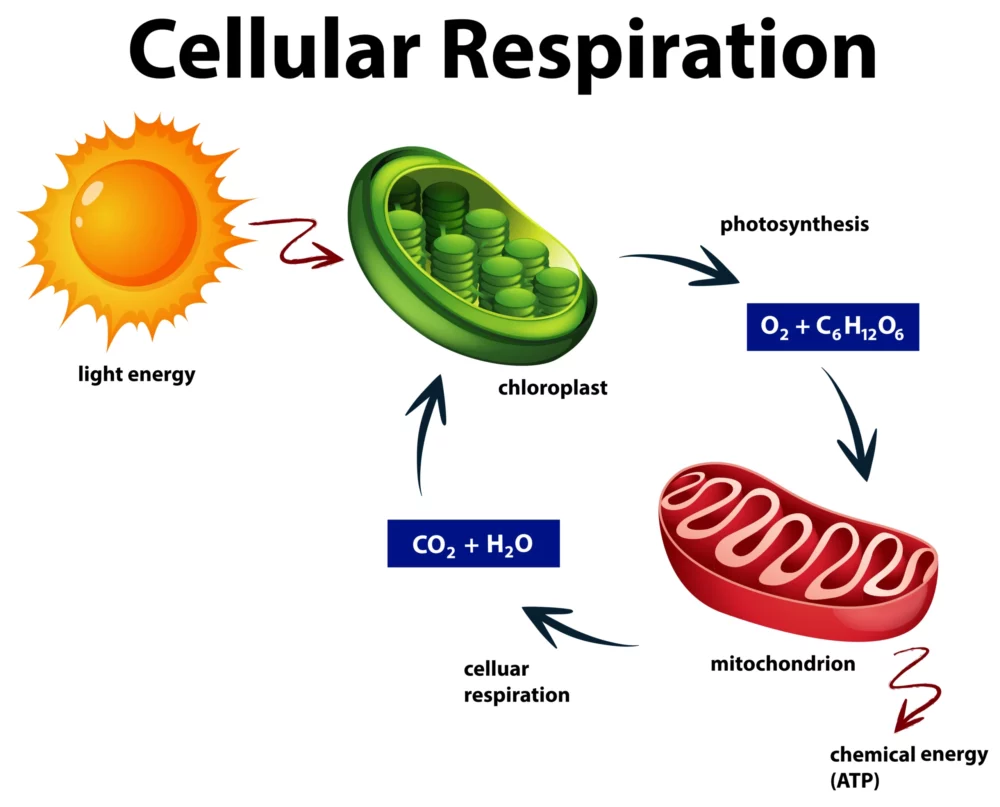
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Cellular respiration is a fundamental biochemical process that occurs in all living cells, from the tiniest bacteria to the most complex multicellular organisms. It is the means by which cells convert organic molecules, primarily glucose, into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – the universal currency of cellular energy. This intricate and highly regulated metabolic pathway is essential…

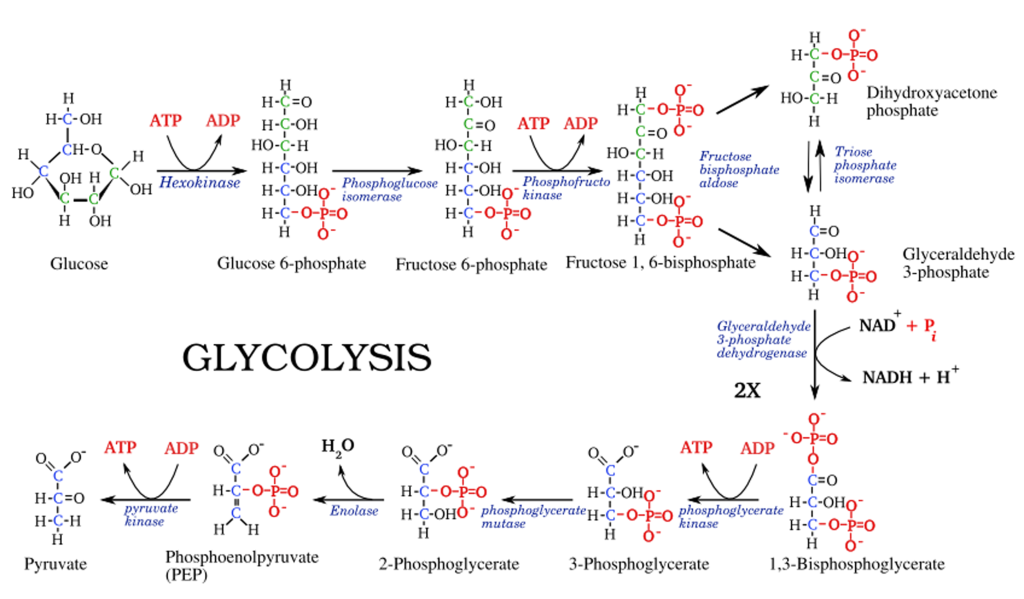
Glycolysis Pathway
Glycolysis is a crucial metabolic pathway found in all living cells, serving as the initial step in the breakdown of glucose to produce energy. This ancient and highly conserved process occurs in the cytoplasm and plays a central role in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. In this note, we’ll delve into the details of glycolysis,…