Tag: Biology notes

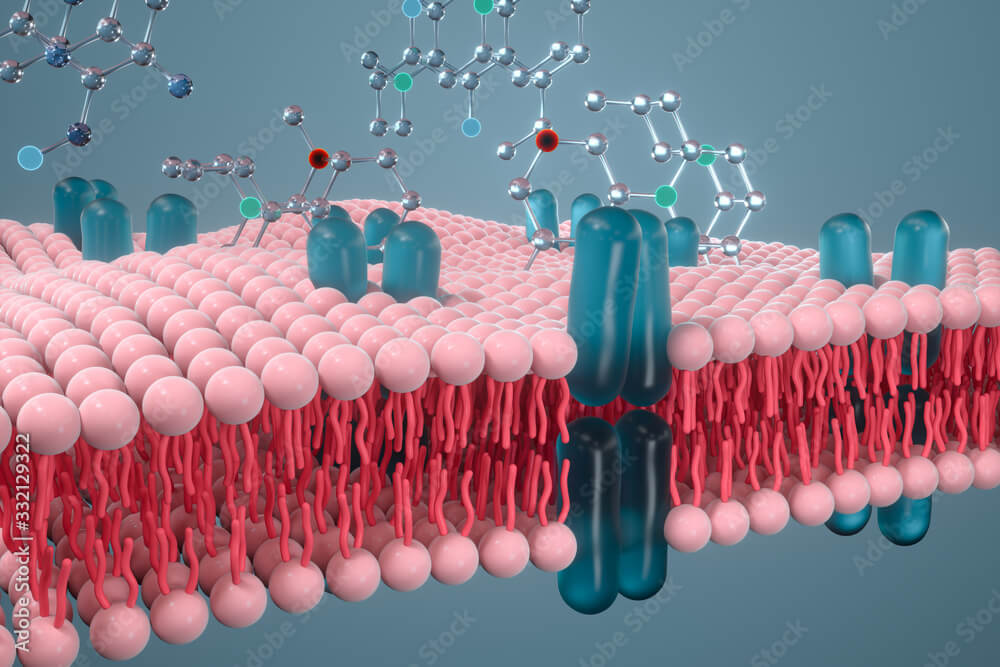
Plasma membrane
Delimiting membrane or boundary of all cells providing the characteristic shape to the cell. Structure ● Composed of approx. 7 nm thick phospholipid bilayer with hydrophilic heads facing outward from both sides into aqueous environment and hydrophobic tails facing inside the bilayer. ● A symmetrical the presence of proteins, floating in the bilayer imparts a…

Chromosome
A chromosome is a structure found in cells that is made up of a long strand of DNA, which is the genetic material that contains the instructions for the development and function of all living organisms. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and play a crucial role in the cell cycle, replication,…

Type of Classification System Quiz
Welcome to our “Type of Classification System Quiz!” Are you ready to explore the diverse methods used to categorize everything from living organisms to data sets? Classification systems are essential tools that help us organize and make sense of the world around us. In this quiz, we’ll dive into various types of classification, from biological…

MCQ on Respiration in plant
Q1: Which organelle in plant cells is primarily responsible for cellular respiration? (A) Chloroplast (B) Mitochondrion (C) Vacuole (D) Nucleus Answer: (B) Mitochondrion Explanation: Mitochondria are the main sites of cellular respiration in plant cells, where ATP is produced. Q2: During respiration, what is the primary substrate used by plants to generate energy? (A) Oxygen…
Ecosystem – Structure and Function
The term ‘ecosystem’ was proposed by a British ecologist A.G. Tansley (1953). It represents the basic fundamental, functional unit of ecology which comprises of the biotic community together with its abiotic (non-living) environment. Ecosystem is the functional unit of nature where living organisms interact with each other and with their environment. Ecosystems can be recognized…
Active Transport
A few ions or molecules are transported across the membrane against their concentration gradient, i.e., from lower to higher concentration. Such type of transport is called active transport because it is an energy-dependent process in which ATP is utilised, e.g., Na+/K+ pump. https://youtu.be/visqfZd7Ms4 Active transport uses energy to pump molecules against a concentration gradient. Active…

EXCRETORY SYSTEM IN HUMAN
Except for urinary bladder which is endodermal in origin, the whole excretory system is Except urinary bladder which is endodermal in origin, the whole excretory system is Except mesodermal. In human the kidney is retroperitoneal i.e., the kidney is located outside the coelomic cavity and is covered by peritoneum (coelomic epithelium) from the ventral side…

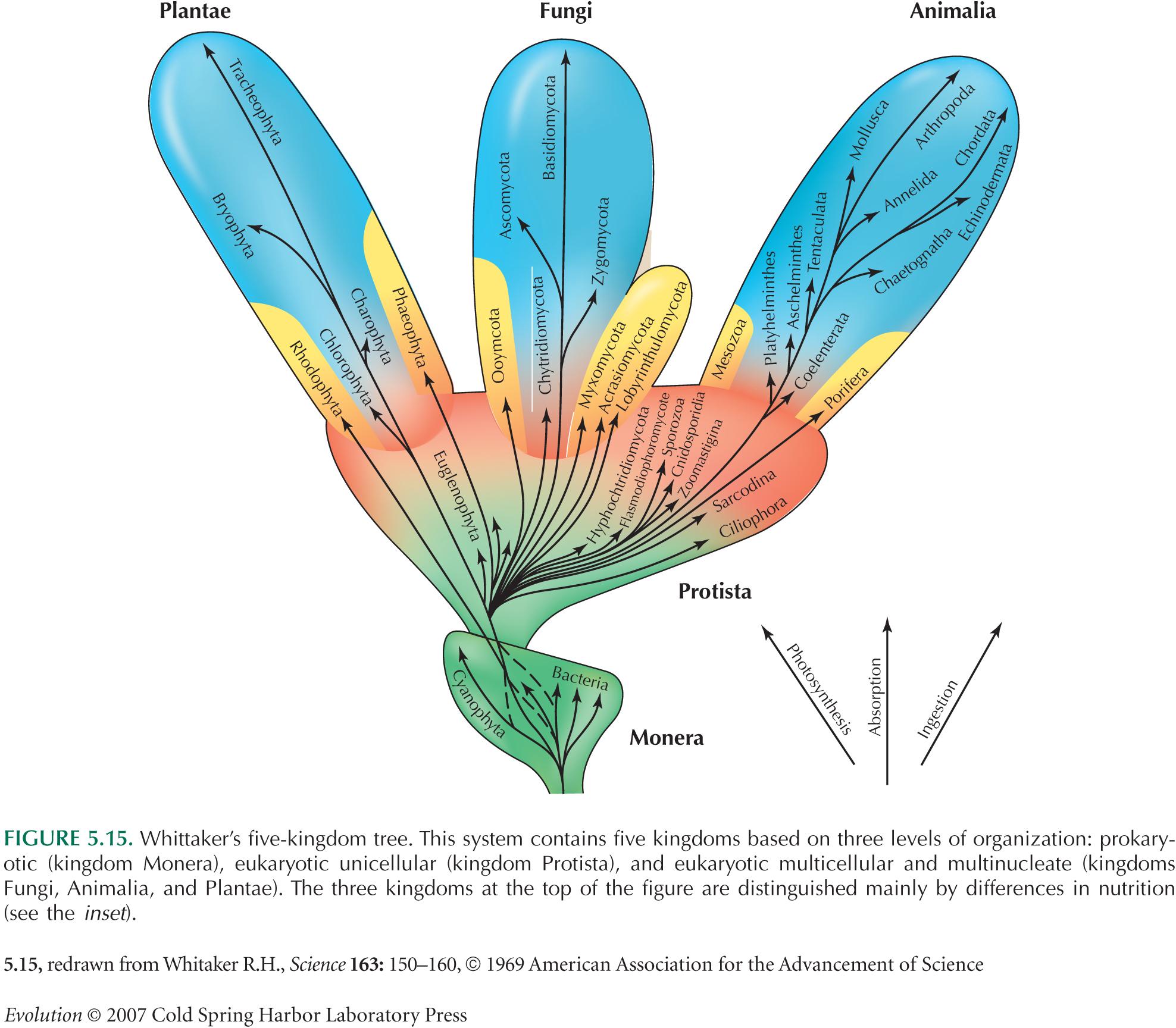
FIVE KINGDOM SYSTEM
In this lesson, we discussing five kingdom classification. Five kingdom classification is proposed by R.H.Whittaker in 1969. the kingdom defined by him were named Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. In this lesson, we show a brief introduction to these kingdoms for more information on kingdom please visit a particular lesson on that kingdom. Main Criteria…

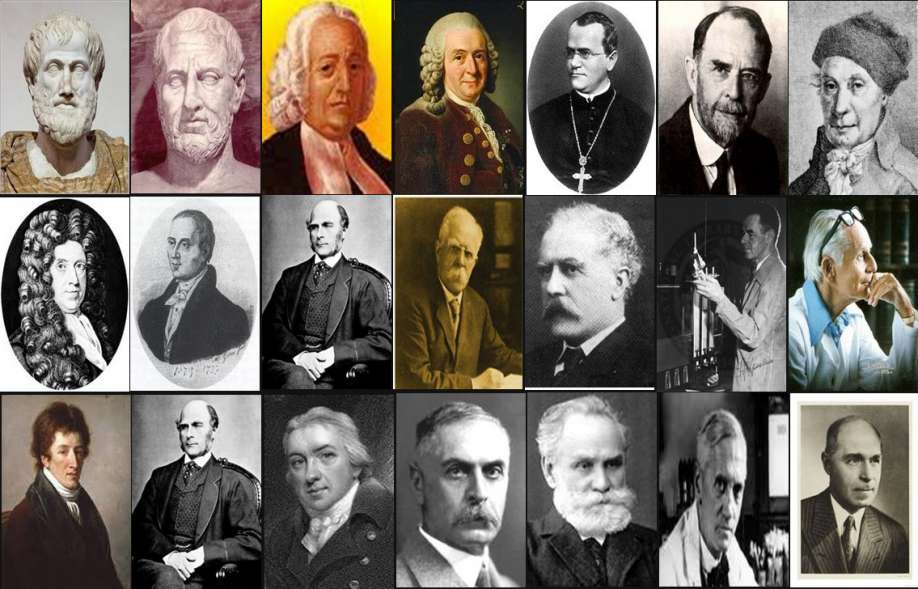
Father of Various Branches of Biology
Father of Agronomy Peter – De- Cresenji Father of Agriculture Norman Borlaug Father of Anatomy Andreas Vesalius Father of Botany Theophrastus Father of Biology Aristotle Father of Bacteriology Antonie van LeeuwenhoekRobert Koch / Ferdinand Cohn / LouisPasteur Father of Blood Groups Karl Landsteiner Father of Blood Circulation William Harvey Father of Cytology Robert Hooke Father…

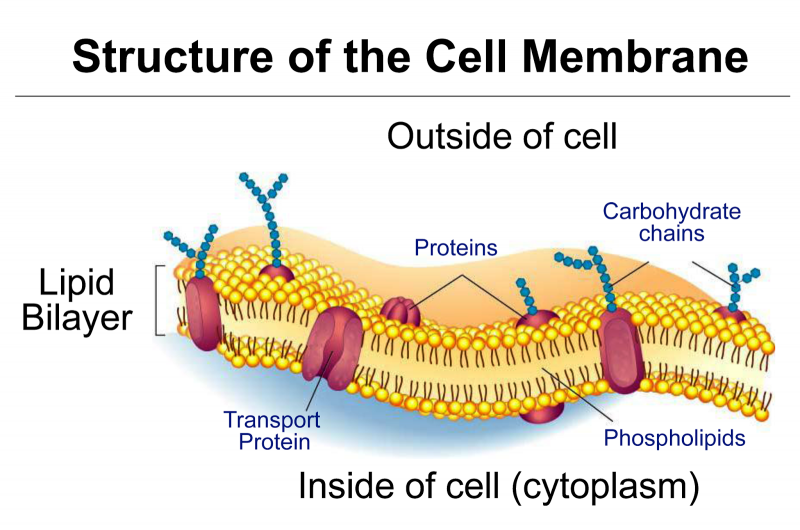
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is otherwise called a Plasma membrane. It may be defined as the thin, elastic, semipermeable living membrane that serves as a boundary for the Cytoplasm. The Cell membrane is made up of glycoproteins and phospholipids. The Functions of the Cell membrane are as follows: Cell membrane or Plasma membrane is a semipermeable membrane present…

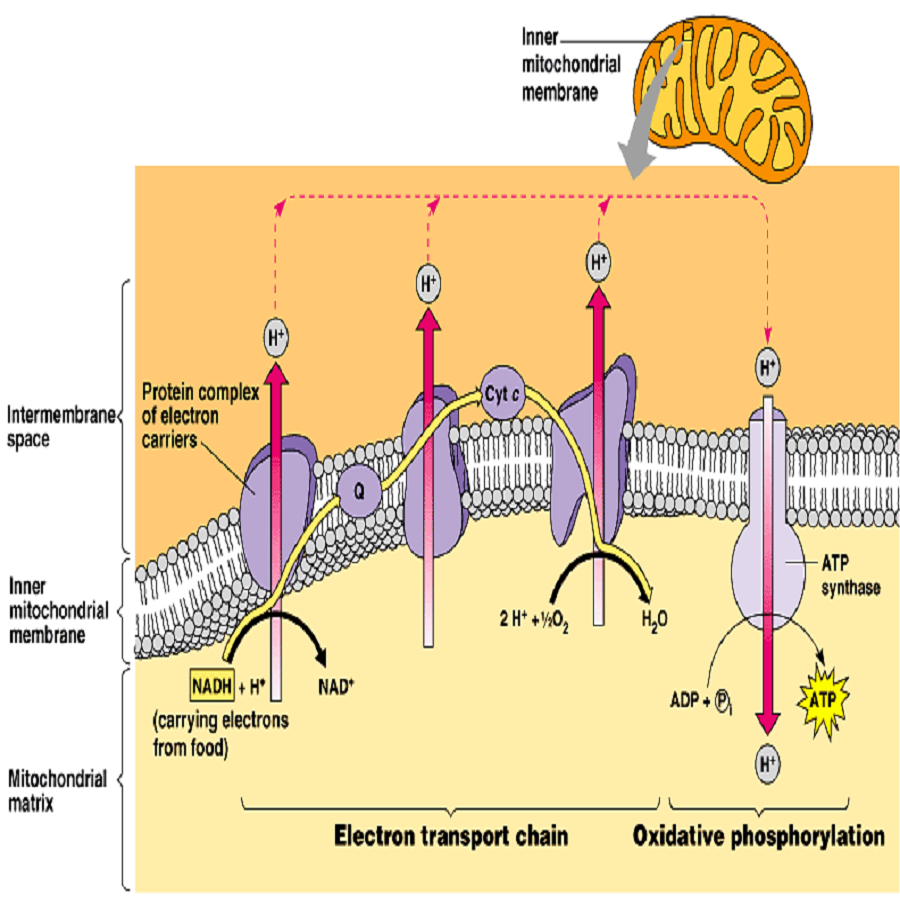
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION, ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION It is the main source of energy of our cell. Takes place in Mitochondria. Movement of protons through inner mitochondrial membrane leads to ATP production DEFINITION Oxidative phosphorylation includes the coupling of the oxidation of NADH or FADH2 by the respiratory chain with the synthesis of ATP via gradient of protons across the inner mitochondrial…

DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
DIFFERENT MODE OF DIGESTION IN ORGANISMS The collective processes by which a living organism takes food which are necessary for their growth, maintenance and energy needs is called nutrition. The chemical substances present in the food are called nutrients. It is important to know the different modes of nutrition in all living organisms in order…