Category: Cell biology

Enzymes: Substrate Interaction & Biochemistry
Within the realm of biology, cells rely on intricate processes to sustain life. Catalysts known as proteins play a crucial role in these processes, expediting chemical reactions. These proteins possess a remarkable capability to interact with specific substances, forming the foundation of biochemistry. In this article, we will explore these proteins and their interactions with…

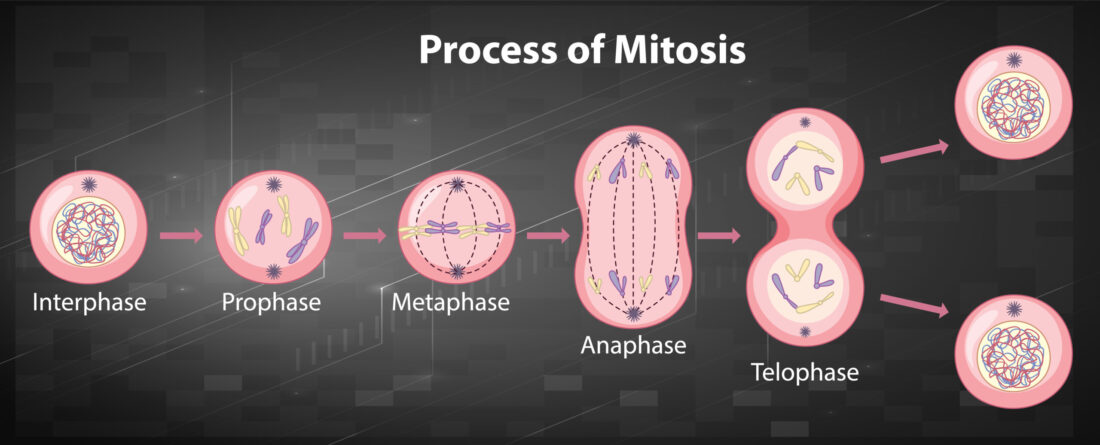
Mitosis: A Comprehensive Explanation of Each Stage and Its Vital Role in Cell Division
Mitosis is a fundamental process of cell division in which a single eukaryotic cell divides into two identical daughter cells, each containing the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process is crucial for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in multicellular organisms. Mitosis consists of several distinct stages, each with its own…

MCQ on Role of Plasma Membrane
here are some multiple-choice questions (MCQs) about “Plasma Membrane Structure and Function: Key Role in Cell Homeostasis,” along with detailed answers: Question 1: Which of the following components make up the plasma membrane’s basic structure? A) Nucleic acids and proteins B) Carbohydrates and lipids C) Proteins and lipids D) Carbohydrates and nucleic acids Answer 1:…

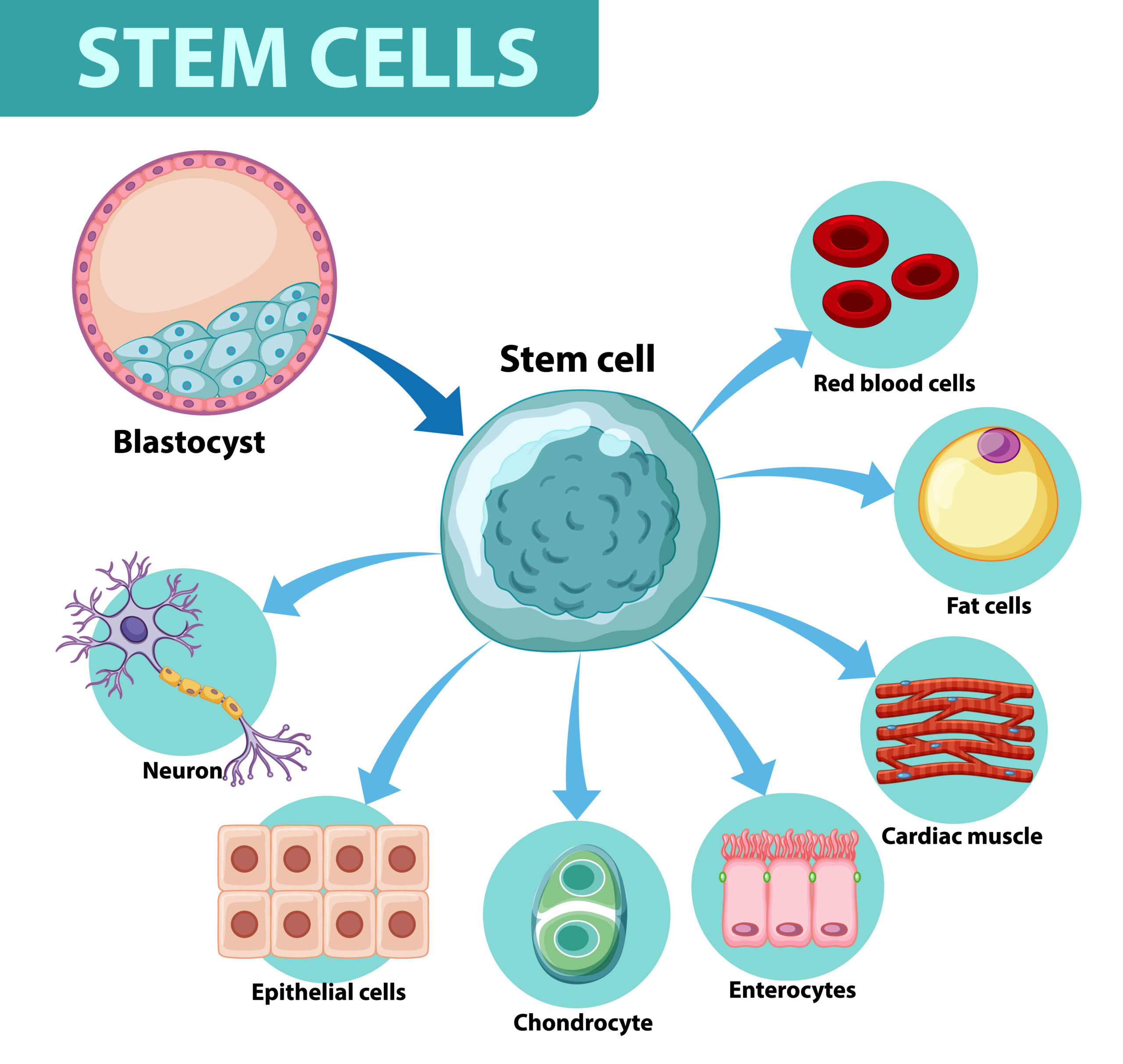
Stem Cells: The Building Blocks of Regeneration
In the intricate tapestry of life, there exists a remarkable group of cells with the potential to reshape our understanding of healing and tissue regeneration. These cells, known as stem cells, have captivated the imagination of scientists and medical researchers for decades due to their unique ability to transform into various cell types and contribute…

What is the role of hemoglobin?
The Crucial Role of Hemoglobin in Your Body Hemoglobin is an unsung hero in your body’s complex orchestra of functions. This iron-rich protein plays a central role in sustaining life by carrying oxygen to every cell. Let’s delve into the fascinating functions of hemoglobin and why it’s essential for your well-being. Oxygen Transport – Hemoglobin’s…

What is enzyme and characteristics?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions in living organisms. They are typically proteins, although some RNA molecules also have catalytic activity. Enzymes are essential for life because they speed up the reactions that are necessary for cells to function properly. Without enzymes, many biochemical reactions in the body would occur too slowly to…

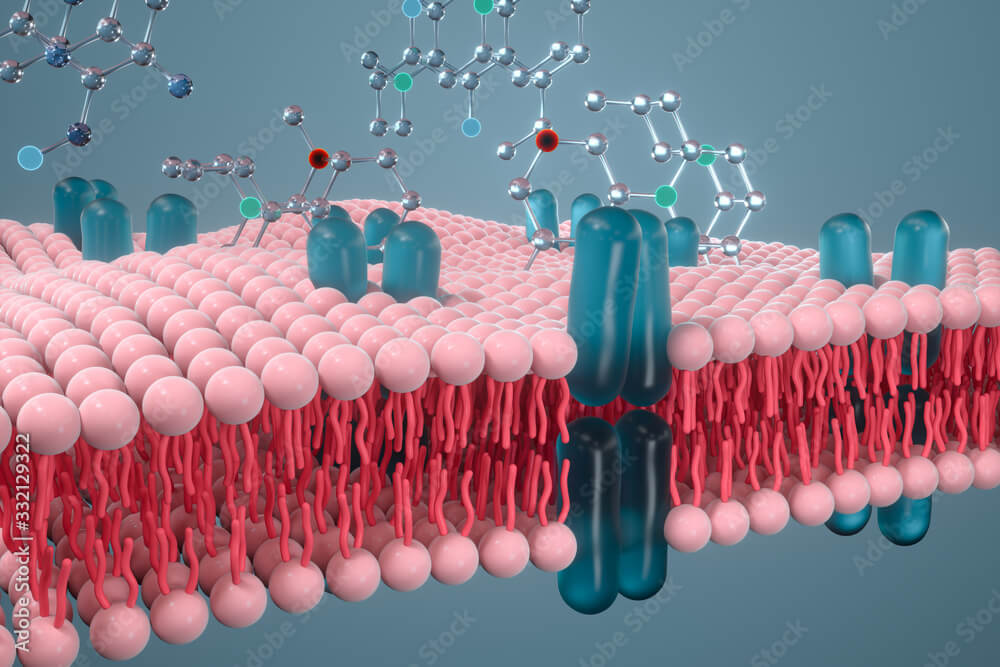
Plasma membrane
Delimiting membrane or boundary of all cells providing the characteristic shape to the cell. Structure ● Composed of approx. 7 nm thick phospholipid bilayer with hydrophilic heads facing outward from both sides into aqueous environment and hydrophobic tails facing inside the bilayer. ● A symmetrical the presence of proteins, floating in the bilayer imparts a…

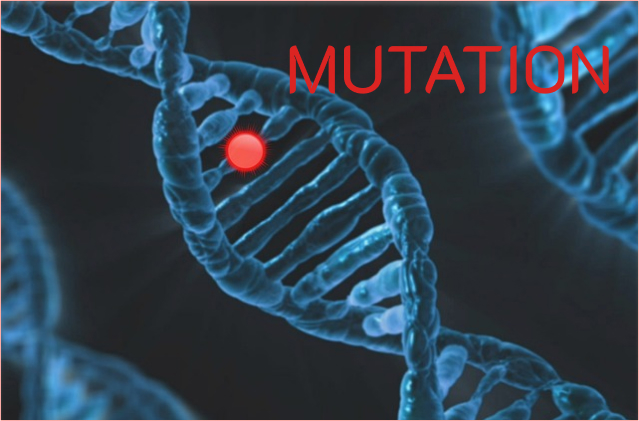
Mutation
Mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of an organism’s genetic material. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule that carries the genetic instructions for the development and function of all living things. DNA is made up of four chemical bases, adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T), which are arranged in…

Chromosome
A chromosome is a structure found in cells that is made up of a long strand of DNA, which is the genetic material that contains the instructions for the development and function of all living organisms. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and play a crucial role in the cell cycle, replication,…

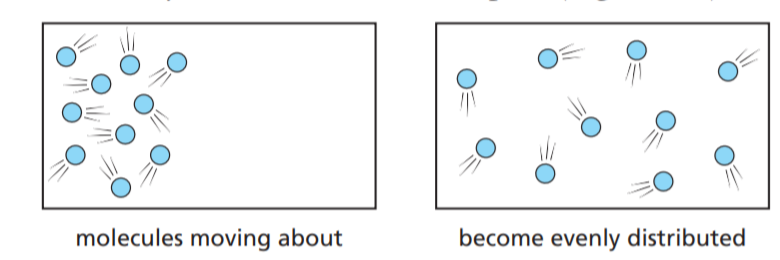
Diffusion – Movement of Substances
Table of Contents Diffusion Defination Diffusion is the net movement of molecules and ions from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration down a concentration gradient, as a result of their random movement. What is Diffusion The molecules of a gas such as oxygen are moving about all the…

MCQ on Respiration in plant
Q1: Which organelle in plant cells is primarily responsible for cellular respiration? (A) Chloroplast (B) Mitochondrion (C) Vacuole (D) Nucleus Answer: (B) Mitochondrion Explanation: Mitochondria are the main sites of cellular respiration in plant cells, where ATP is produced. Q2: During respiration, what is the primary substrate used by plants to generate energy? (A) Oxygen…
CELL JUNCTION
The cells of epithelial and other tissues are held together by various types of cell junctions, that can be categorized into 3- main groups – (I) Adhesive junctions The cells of epithelial tissue and even cardiac muscles are difficult to separate due to the presence of adhesive junctions. Such junctions are of 2-types (a) Adherens…