Category: Cell biology

BLOOD CLOTTING (HAEMOSTASIS)
The clot or coagulam is a dark -reddish-brown ‘scum’ formed mainly by a network of threads in which dead or damaged blood elements are trapped. It is the property of plasma. Normal blood clotting time is 3−10 min. The clot inside the blood vessels is called a thrombus. A moving thrombus is called embolus. In…

CARBOHYDRATES
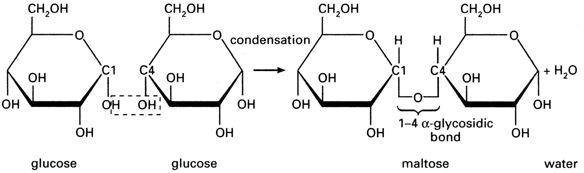
Table of Contents Carbohydrates are classified into two types on the basis of molecular weight. Micromolecules – Monosaccharides and Oligosaccharides (Including Disaccharides) Macromolecules – Polysaccharides The micromolecules have the molecular weight of < 1000 Daltons whereas themacromolecules have > 1000 Daltons as molecular weight. Why do we need carbohydrates in our food? Carbohydrates provides about…

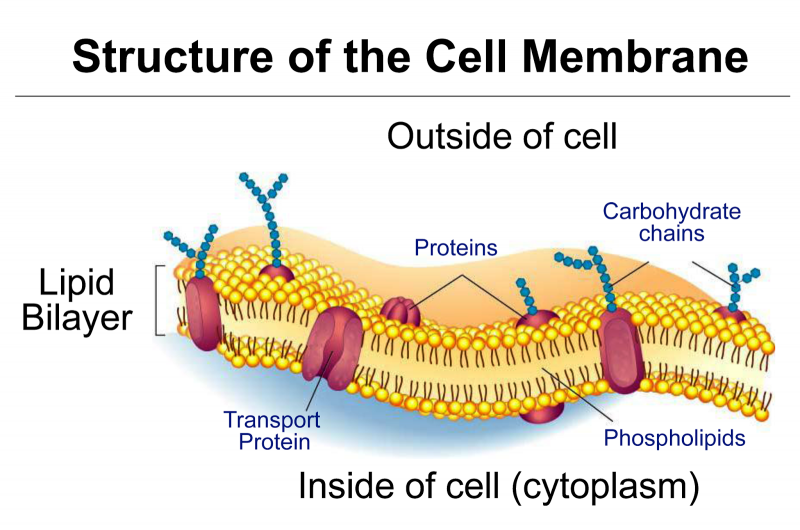
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is otherwise called a Plasma membrane. It may be defined as the thin, elastic, semipermeable living membrane that serves as a boundary for the Cytoplasm. The Cell membrane is made up of glycoproteins and phospholipids. The Functions of the Cell membrane are as follows: Cell membrane or Plasma membrane is a semipermeable membrane present…
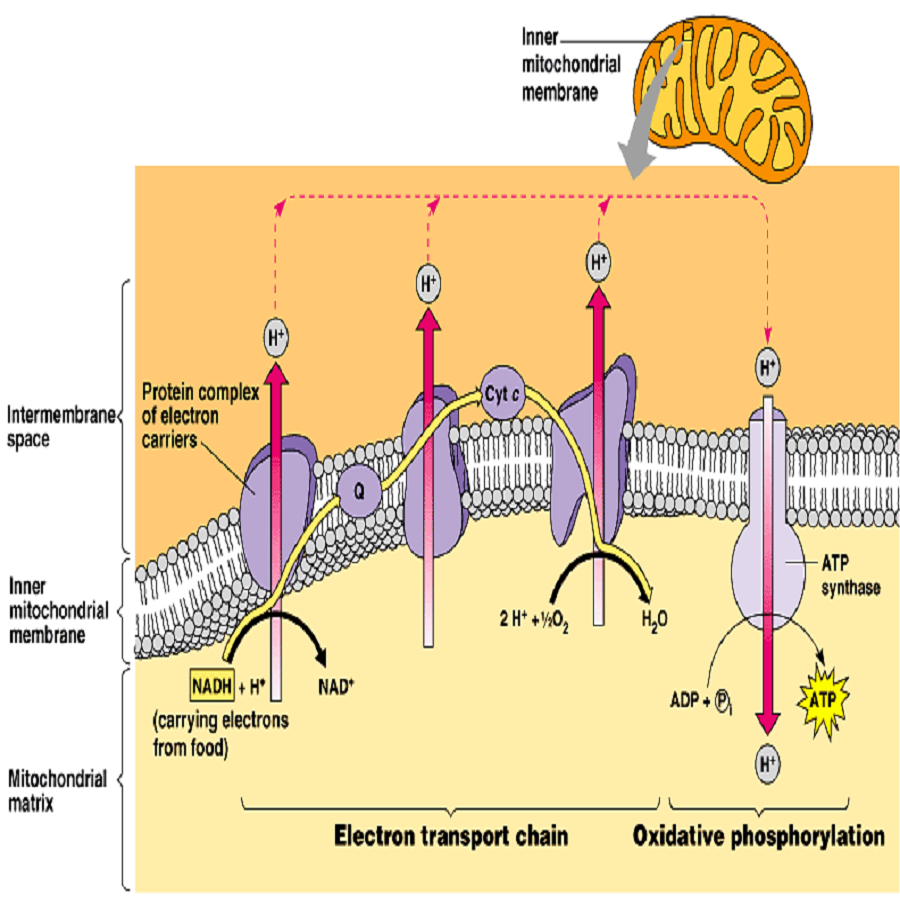
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION, ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION It is the main source of energy of our cell. Takes place in Mitochondria. Movement of protons through inner mitochondrial membrane leads to ATP production DEFINITION Oxidative phosphorylation includes the coupling of the oxidation of NADH or FADH2 by the respiratory chain with the synthesis of ATP via gradient of protons across the inner mitochondrial…
ANIMAL TISSUE
As mentioned earlier, cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues. Tissues provide the numerous functions of organs necessary to maintain biological life. This lab exercise seeks to introduce the various tissues found in the human body and…

HOMEOSTASIS
Q1) The relationship between mineral and water is know as: A) Ascent of sap B) Osmoregulation C) Excretion D) All of them Q2) The cell sap having solution of: A) One types B) Two types C) Three types D) Four types Q3) The water potential not more than: A) 1 B) 100 C) 1000 D)…

EXCRETION
Q1) Unwanted substances excreted by plants are: A) Uric acid B) Ammonia C) Latex D) Urea Q2) Solid crystalline substance called uric acid excreted as Solid waste in: A) Insects B) Planty helminthes C) Vertebrates D) Annelids Q3) Nephrons are connected with: A) Respiratory system B) Nervous system C) Circulatory system D) Excretory system Q4) Which…

OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION, ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION It is the main source of energy of our cell. Takes place in Mitochondria. Movement of protons through inner mitochondrial membrane leads to ATP production DEFINITION Oxidative phosphorylation includes the coupling of the oxidation of NADH or FADH2 by the respiratory chain with the synthesis of ATP via gradient of protons across the inner mitochondrial…

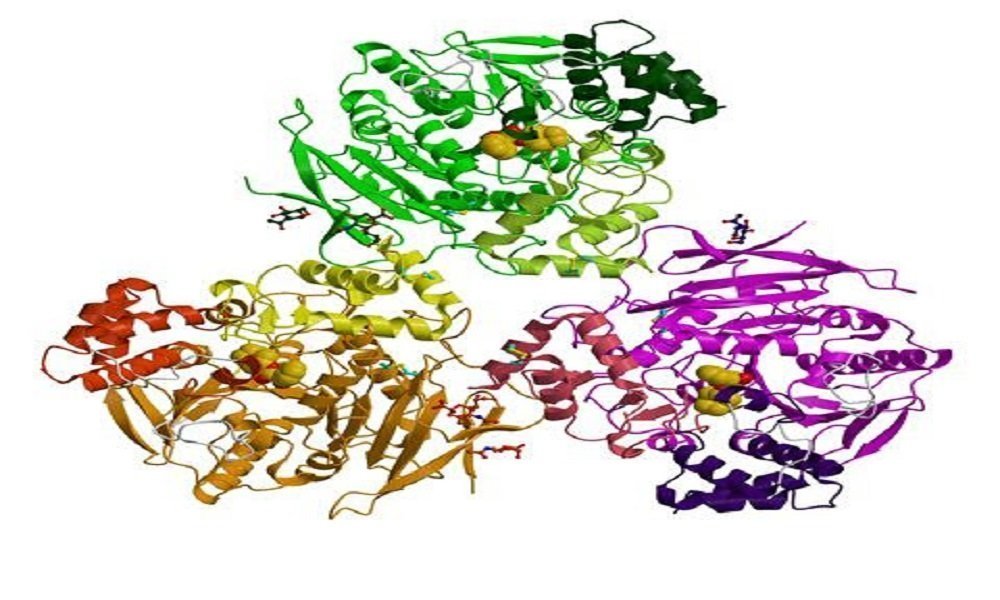
ENZYMES
The global life depends on a series of chemical reactions. Most of the chemical reactions proceed too slowly on their own to sustain life. Hence catalysts are required to greatly accelerate the rates of these chemical reactions. In nature enzymes posses the catalytic power to facilitate life processes in essentially all life-forms from viruses to…

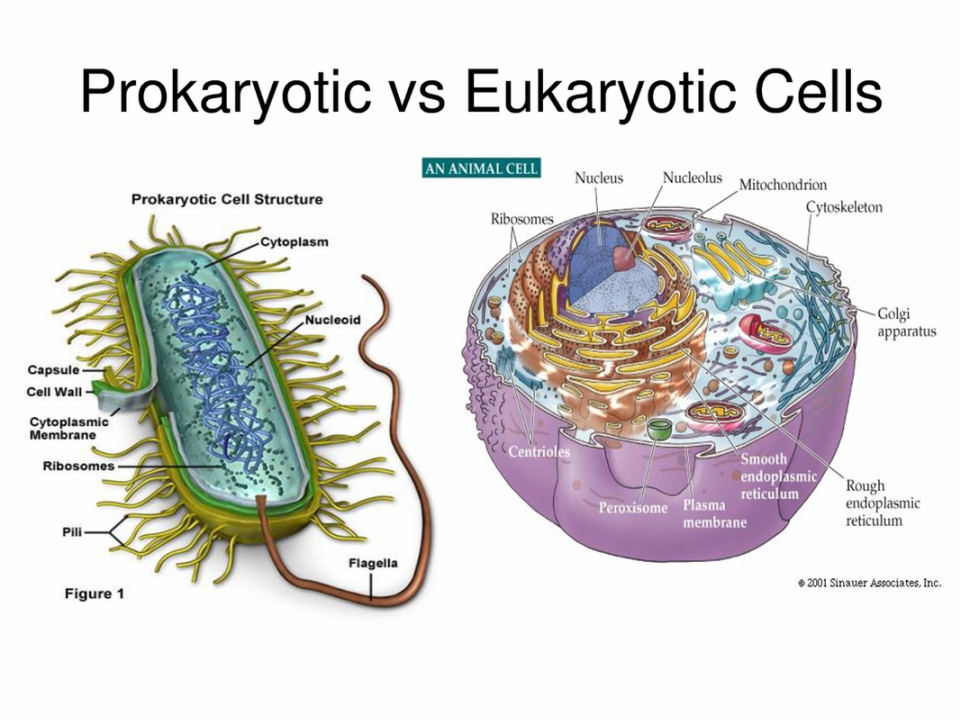
THE CELL AND CELL THEORY
Landmarks in the study of a cell Soon after Anton Van Leeuwenhoek invented the microscope, Robert Hooke in 1665 observed a piece of cork under the microscope and found it to be made of small compartments which he called “cells” (Latin cell = small room). In 1672, Leeuwenhoek observed bacteria, sperms and red blood corpuscles,…

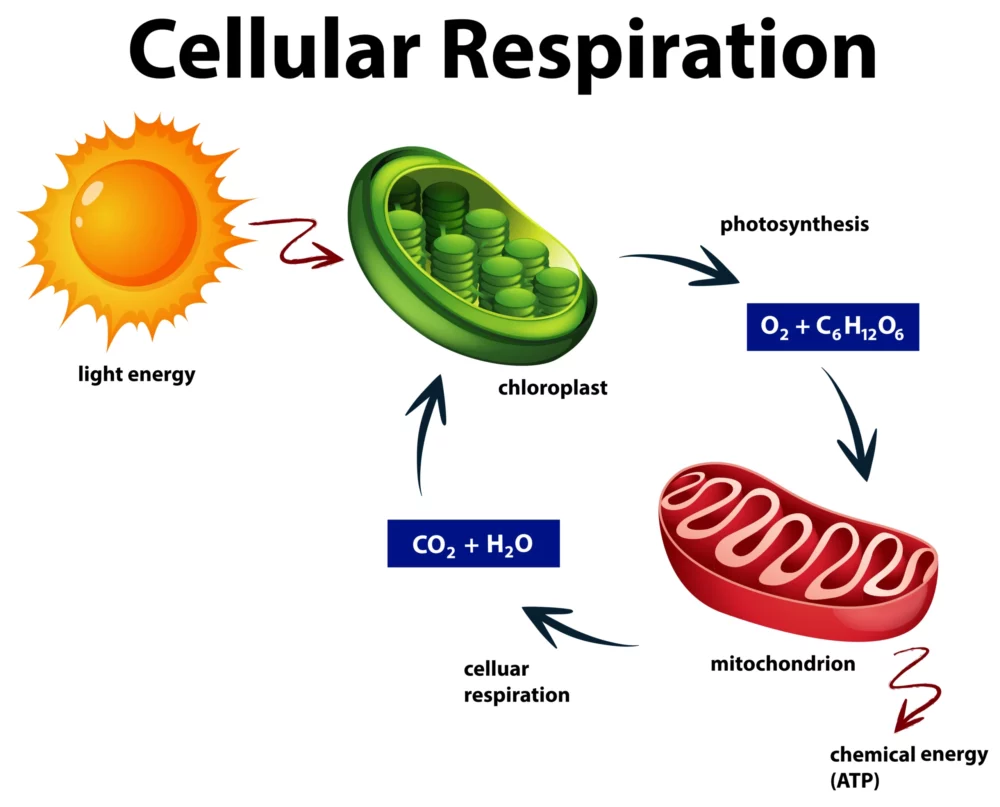
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Cellular respiration is a fundamental biochemical process that occurs in all living cells, from the tiniest bacteria to the most complex multicellular organisms. It is the means by which cells convert organic molecules, primarily glucose, into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – the universal currency of cellular energy. This intricate and highly regulated metabolic pathway is essential…

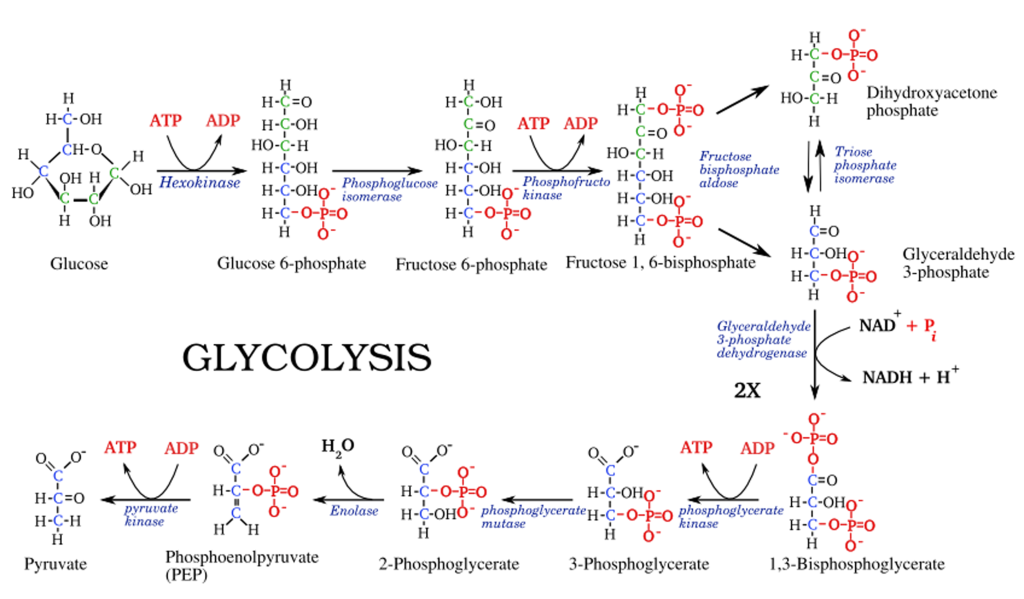
Glycolysis Pathway
Glycolysis is a crucial metabolic pathway found in all living cells, serving as the initial step in the breakdown of glucose to produce energy. This ancient and highly conserved process occurs in the cytoplasm and plays a central role in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. In this note, we’ll delve into the details of glycolysis,…