One stop solution for all your biology questions!

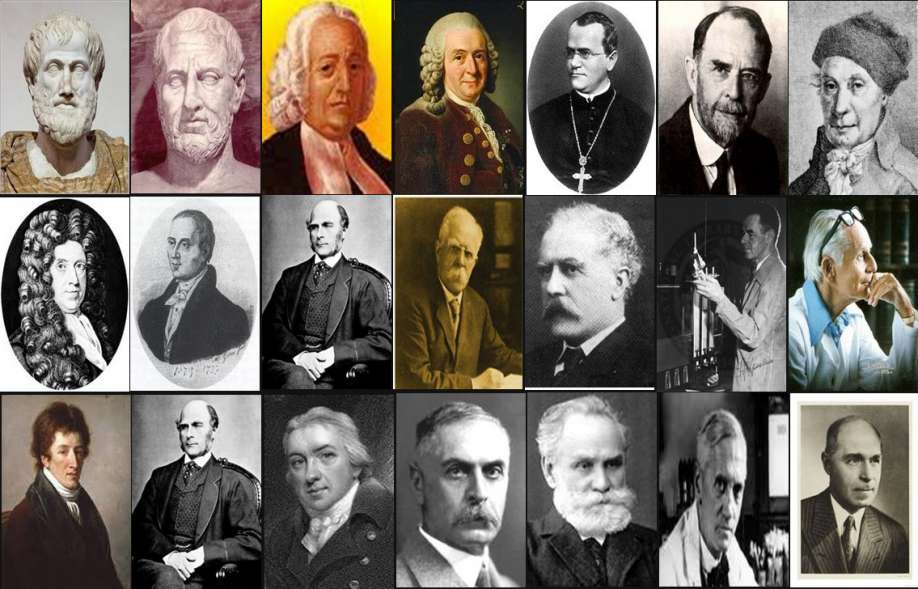
Father of Various Branches of Biology
Father of Agronomy Peter – De- Cresenji Father of Agriculture Norman Borlaug Father of Anatomy Andreas Vesalius Father of Botany Theophrastus Father of Biology Aristotle Father of Bacteriology Antonie van LeeuwenhoekRobert Koch / Ferdinand Cohn / LouisPasteur Father of Blood Groups Karl Landsteiner Father of Blood Circulation William Harvey Father of Cytology Robert Hooke Father…

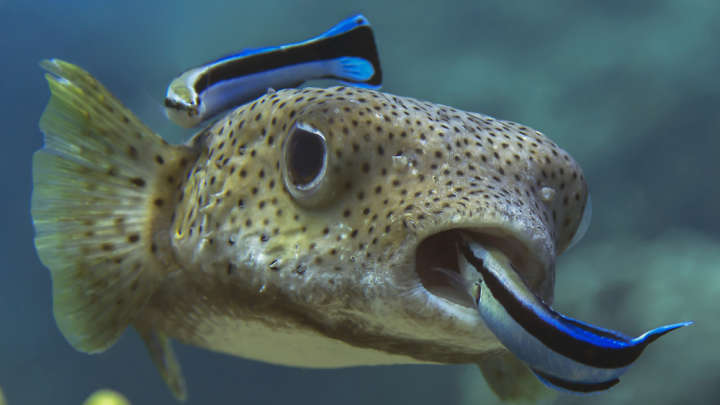
Symbiosis
A symbiosis is an evolved interaction or close living relationship between organisms from different species, usually with benefits to one or both of the individuals involved. Symbioses may be ‘obligate’, in which case the relationship between the two species is so interdependent, that each of the organisms is unable to survive without the other, or…

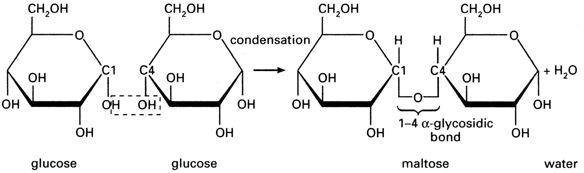
CARBOHYDRATES
Table of Contents Carbohydrates are classified into two types on the basis of molecular weight. Micromolecules – Monosaccharides and Oligosaccharides (Including Disaccharides) Macromolecules – Polysaccharides The micromolecules have the molecular weight of < 1000 Daltons whereas themacromolecules have > 1000 Daltons as molecular weight. Why do we need carbohydrates in our food? Carbohydrates provides about…
MCQs ON PLANT KINGDOM
1. Sexual reproduction involving the fusion of two cells in Chlamydomonas is (a) isogamy (b) homogamy (c) somatogamy (d) hologamy Answer and Explanation: 1. (d): Isogamy involves the fusion of gametes which are morphologically and physiologically similar. They are called isogametes. In Chlamydomonas, two vegetative cells may fuse to form a zygospore and the phenomenon is…

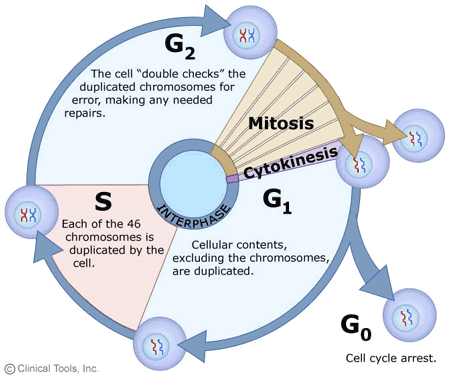
Q & A ON CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
Q 1. Define cell cycle Ans. The sequence of events by which cell duplicates its genome, synthesis of other constituents of the cell and eventually divides into two daughters cell. Q2. Name the phases of cell cycle Ans. A) Interphase B) M Phase Q3. What is the G1phase of the interphase? Ans. The G1 phase Corresponds to interval…

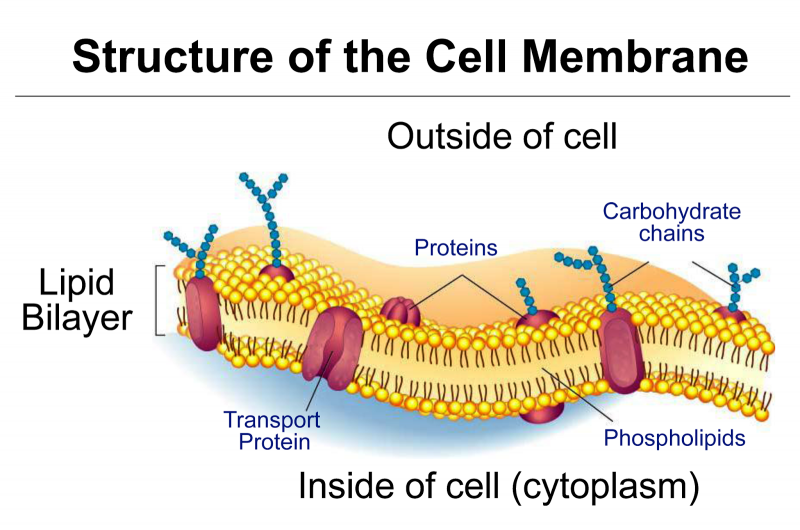
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is otherwise called a Plasma membrane. It may be defined as the thin, elastic, semipermeable living membrane that serves as a boundary for the Cytoplasm. The Cell membrane is made up of glycoproteins and phospholipids. The Functions of the Cell membrane are as follows: Cell membrane or Plasma membrane is a semipermeable membrane present…

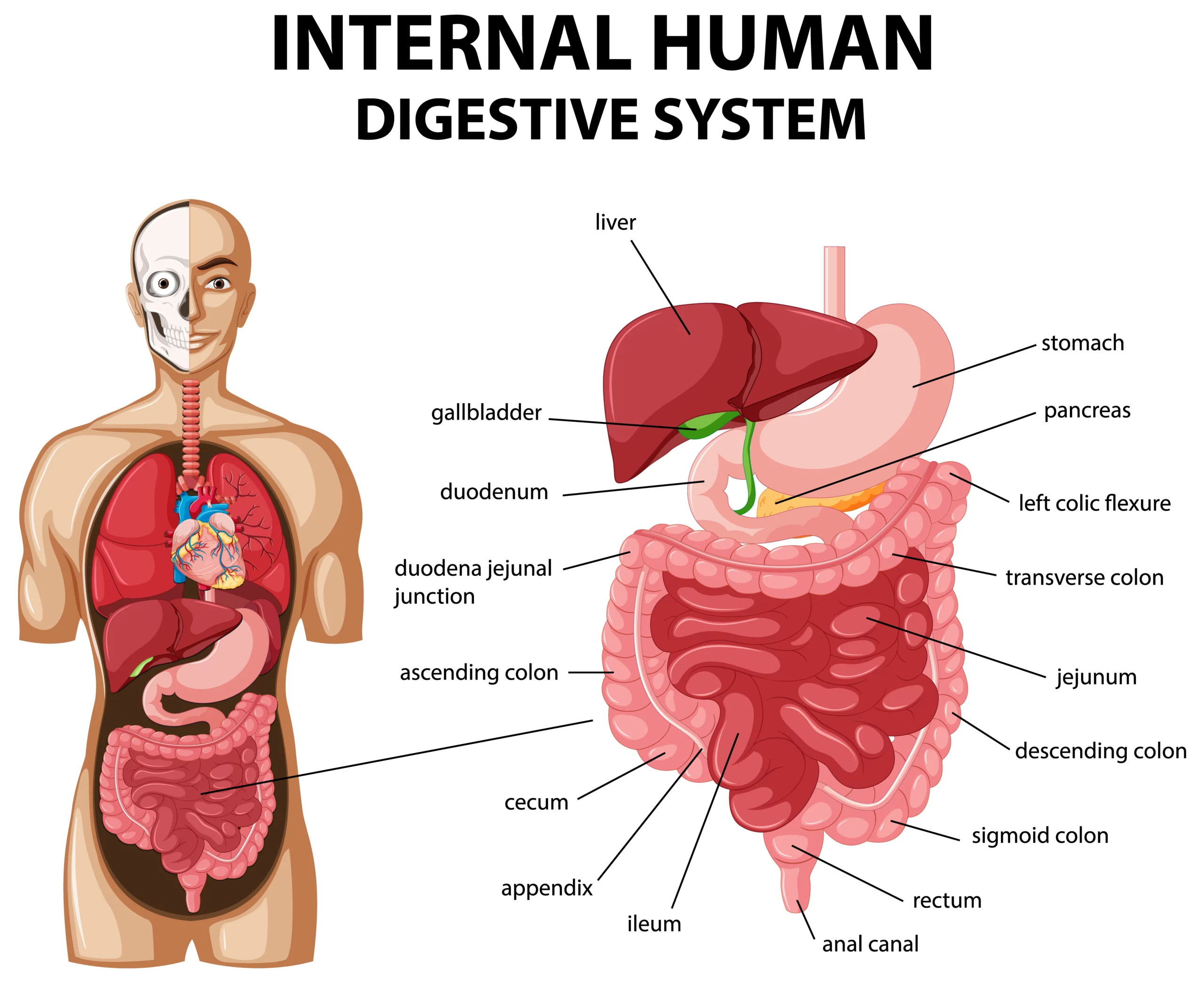
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Navigating the Human Digestive System: Your Food’s Amazing Journey Our bodies are incredible, and one of the most intriguing systems within them is the digestive system. This system does the important job of turning the food we eat into energy and nutrients that fuel our bodies. Let’s take a fascinating tour through the human digestive…
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION, ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION It is the main source of energy of our cell. Takes place in Mitochondria. Movement of protons through inner mitochondrial membrane leads to ATP production DEFINITION Oxidative phosphorylation includes the coupling of the oxidation of NADH or FADH2 by the respiratory chain with the synthesis of ATP via gradient of protons across the inner mitochondrial…
ANIMAL TISSUE
As mentioned earlier, cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues. Tissues provide the numerous functions of organs necessary to maintain biological life. This lab exercise seeks to introduce the various tissues found in the human body and…

Q & A ON REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
Q1. What is life span? Ans: Life span is the period from birth to natural death of an organism. Q2. Define clone. Ans: The individuals that are morphologically and genetically similar to the parent are called clone. Q3. Mention the different means/ methods of asexual reproduction with example. Ans: Cell division – Protista, Monera Binary…
Q & A ON WATER AND MINERAL SALT
Q1. What is the approximate percentage (in mass) of water in the human body? Is this percentage expected to be larger in the adult or in the old individual? Ans: Approximately 65% of the human individual mass is water. The brain, for example, has around 90% of water in mass, the muscles, 85%, and the…
Q & A OF ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS
Q1) Name the associated structure of companion cell. Ans: Sieve tube cell Q2) Name an enucleated plant cell. Ans: Sieve tube cell Q3) Name the conductory elements of xylem. Ans: Tracheary elements- Tracheids and Vessels (tracheae) Q4) What is periderm? Ans: Phellogen, Phellum and Phelloderm are collectively called as Periderm Q5) What is annual ring?…